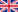
An analysis of optimal segmented flight design in a rotary dryer
In this paper, an analysis of the optimal design for two-segmented flight is performed with the aim to obtain some practical recommendations for the design of a rotary dryer. Using a geometrical model, validated with experimental results, flight loading and unloading are studied over the range of every possible angle between the flight segments. Maximum volume carried out by the flight, the maximum discharging angle and the mean falling height of material are computed for all configurations. Influence of size ratio between segments and drum radius are also investigated. By determining the curtain filling degree and the cumulative transfer area of material over one drum revolution, we estimate what the best flight design is, in order to maximise the contact surface between material and air flow necessary to increase the dryer performance.
Two-scale analysis of the permeability of 3D periodic granular and fibrous media
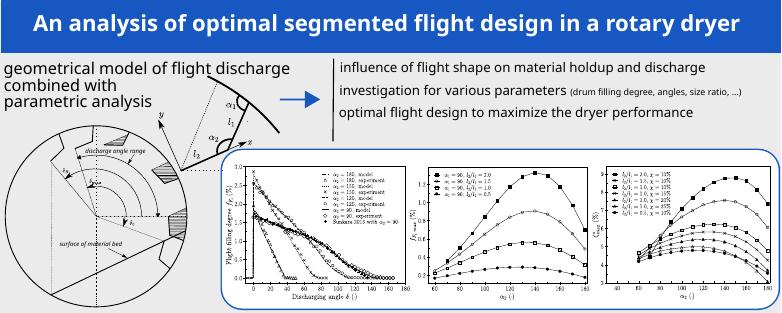
Two-scale analysis of the permeability of 3D periodic granular and fibrous media
In this paper, a numerical study of slow flow through a filter viewed as a porous medium made of arrays of cubic solid particles or solid fibers of square cross section is considered. A double-scale asymptotic method is used to determine a system of equations that are then solved numerically to calculate the permeability. Simulations are made at the REV scale, and macroscopic properties are deduced. At the microscale, three arrangements (simple cubic, body-centered cubic and face-centered cubic) are analyzed. A parametric study is carried out, for both granular and fibrous cases, showing the porosity evolution with the size ratio between the solid particles and the periodic cell. At the macroscopic scale, the interest of this analysis is to compute the Darcy’s permeability of such arrays as a function of the porosity and the packing characteristics. Results are given over the full porosity range for SC, BCC and FCC arrays. On the other side, the microscopic analysis shows the influence of particle or fiber arrangement and size on the fluid velocity and the pressure field inside the porous structure.
Modeling of fluid-solid interaction in granular media with coupled lattice Boltzmann/discrete element methods: application to piping erosion
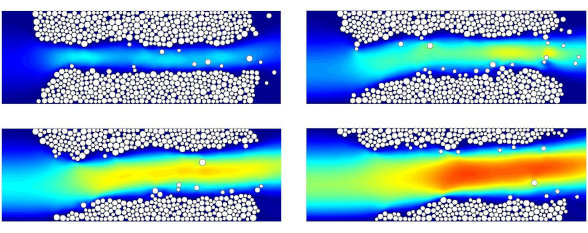
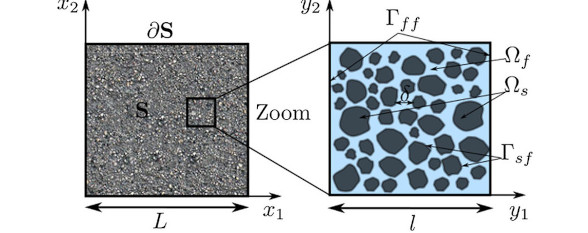
Abstract : In this article, we present a numerical method to deal with fluid-solid interactions and simulate particle-fluid systems as encountered in soils. This method is based on a coupling between two methods, now widely used in mechanics of granular media and fluid dynamics respectively: the discrete element (DE) method and the lattice Boltzmann (LB) method. The DE method is employed to model interactions between particles, whereas the LB method is used to describe an interstitial Newtonian fluid flow. The coupling presented here is a full one in the sense that particle motions act on fluid flow and reciprocally. This article presents in details each of the two methods and the principle of the coupling scheme. Determination of hydrodynamic forces and torques is also detailed, and the treatment of boundaries is explained. The coupled method is finally illustrated on a simple example of piping erosion, which puts in evidence that the combined LB-DE scheme constitutes a promising tool to study coupled problems in geomechanics.
One random publication paper
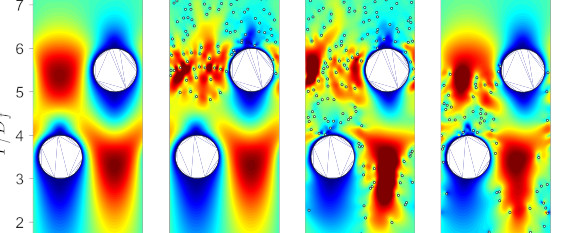
Numerical investigation of the influence of fiber geometry on filtration performance with a coupled LB-DE method
Motion and deposition of solid particles in fibrous filter with circular, diamond, and square fibers are numerically investigated. A coupled Lattice Boltzmann (LB) and discrete element (DE) method is presented and applied to simulate the filtration process in particulate flow, taking into account the mutual interaction between fluid and particle. The influence of pertinent parameters such as the Reynolds number, the particle-to-fiber diameter ratio, and the particle-to-fluid density ratio on filtration performance (pressure drop and capture efficiency) is analyzed for fibrous filter with different fiber cross-sectional shapes. The simulation results indicate that both the pressure drop and the capture efficiency of filter are considerably affected by the fiber’s shape. Dimensionless drag force increases with the Reynolds number when Re > 1. The filter with diamond fiber has a lower pressure drop than that of the circular and square cases. Meanwhile, the deposition of particles on the surface of square fiber is more favorable. From the filter quality factor standpoint, filter with diamond fiber exhibits a better filtration performance.
Phenomenological interpretation of internal erosion in granular soils froma discrete fluid-solid numerical model
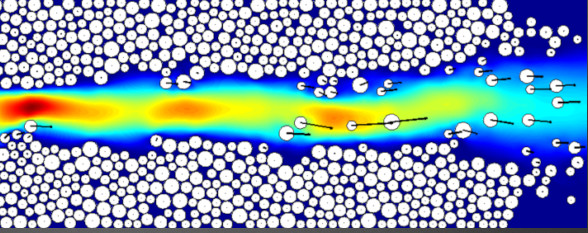
Abstract : Internal erosion in granular soils may involve different steps: the detachment of solid particles from the granular skeleton under the action of water seepage; the transport of the detached particles carried with the water flow in the pore space; and eventually, for some erosion processes, such as suffusion, the possible reattachment of some transported particles to the solid skeleton of the soil, acting as a filter. The first part of this paper is devoted to the description and interpretation of the first step about the particle detachment. The analysis is mainly based on direct numerical simulations performed with a fully coupled discrete element-lattice Boltzmann method. Dynamics of the solid granular phase is represented thanks to the discrete element method in which each solid particle is explicitly described, whereas dynamics of the interstitial water flow is solved with the lattice Boltzmann method. Interactions between the solid phase and the fluid phase are handled at the particle scale avoiding the introduction in the model of some phenomenological constituents to deal with fluid-solid interactions. Numerical modellings of hole erosion can be interpreted similarly to laboratory hole erosion tests where the erosion rate is linearly related to the hydraulic shear stress. Further investigations from the numerical results suggest that the erosion rate ...
Dispersion of particles by spontaneous interparticle percolation through unconsolidated porous media
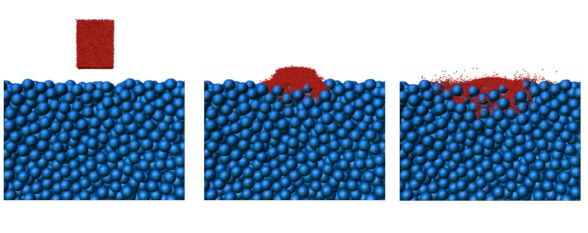
Abstract : We have performed extensive experimental and numerical studies of spontaneous percolation of small beads through an unconsolidated porous media made with large glass beads. In this paper, an experimental setup and a fast "discrete element method" algorithm are presented to deal with large numbers of particles during our interparticle percolation phenomenon studies. In all the experimental and numerical analyses, the size ratio between the moving beads and the stable packing was chosen larger than the geometrical trapping threshold: ξc=((2/(√3−1))^−1=6.464.... We measure the longitudinal and transverse dispersion coefficients versus the height of the porous medium or the number of falling small beads. The influence of bead properties such as density, diameter, or restitution coefficients was investigated by using either steel or glass beads. The individual description of these effects and their explanations were made possible by confrontation and coupling between experimental and numerical results. Indeed, with our numerical model, individual analysis of the effects of these mechanical or geometrical parameters were made possible and carried out.